1 国防科技大学 电子对抗学院 脉冲功率激光技术国家重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230037
2 国防科技大学 电子对抗学院 先进激光技术安徽省实验室,安徽 合肥 230037
3 电磁空间安全全国重点实验室,天津 300308
4 北京航天控制仪器研究所,北京 100094
研究中红外波段激光对CMOS图像传感器的辐照效应,对探索空间态势感知系统光学成像器件的激光干扰和损伤条件具有重要**意义。开展了不同重频下2.79 μm中红外激光对CMOS图像传感器的干扰与损伤实验。观察到CMOS图像传感器的饱和、过饱和以及损伤产生的绿屏、彩色条纹、黑屏、亮线等一系列干扰损伤现象。同时测量了传感器各种辐照现象相对应的2.79 μm中红外激光干扰损伤阈值,研究了图像传感器辐照效应与激光重频之间的内在关系,分析了2.79 μm中红外激光对CMOS图像传感器的干扰损伤机理。研究表明,CMOS图像传感器的激光损伤主要以材料的热熔融为主,热效应明显。在激光重频10 Hz的辐照下,饱和干扰阈值为0.44 J/cm2、过饱和阈值为0.97 J/cm2、损伤阈值为203.71 J/cm2。研究表明CMOS图像传感器具有很好的抗干扰和抗损伤能力,实验测得的相关阈值数据在空间激光攻防领域具有重要的参考价值。
中红外激光 辐照效应 CMOS图像传感器 损伤阈值 mid-infrared laser irradiation effect CMOS image sensor damage threshold 红外与激光工程
2023, 52(6): 20230168
1 光电信息控制和安全技术重点实验室, 天津
2 中国人民解放军93046部队, 沈阳
作为光纤非线性效应中的一种, 孤子自频移效应由于其特殊的脉冲自持性而成为光纤中超短脉冲波长调谐的有效方式。从理论计算和实验验证角度对光纤中的孤子自频移效应进行研究, 基于广义非线性薛定谔方程对光纤中的孤子自频移效应进行仿真计算, 通过测量超短脉冲在保偏光子晶体光纤输出端的光谱对其进行实验分析, 理论和实验结果相符合, 均表明基于孤子自频移效应的超短脉冲波长可以实现大于300 nm的光纤反常色散区连续调谐。
孤子自频移 超短脉冲 波长调谐 光子晶体光纤 soliton self-frequency shift effect ultrashort pulse wavelength tuning photonic crystal fiber

Guanhua Liang 1,2,3Junfeng Jiang 1,2,3,*Kun Liu 1,2,3Shuang Wang 1,2,3[ ... ]Tiegen Liu 1,2,3,4
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Precision Instruments and Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Institute of Optical Fiber Sensing of Tianjin University, Tianjin Optical Fiber Sensing Engineering Center, Tianjin 300072, China
3 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronics Information Technology (Tianjin University), Ministry of Education, Tianjin 300072, China
4 e-mail: tgliu@tju.edu.cn
A phase demodulation method for quasi-distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) systems based on a dual-identical-chirped-pulse and weak fiber Bragg gratings (WFBGs) is proposed. Compared to the use of Rayleigh backscattering light in optical fibers, the implementation of WFBGs can contribute to obtaining an optical signal with a higher signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The dual-identical-chirped-pulse is generated by a time-delay fiber, and the sinusoidal carrier is generated by the interference between the two chirped pulses reflected by adjacent WFBGs. The phase of the sinusoidal carrier represents the dynamic strain change posed on the sensing fiber. Discrete Fourier transform is used to directly retrieve the phase information. The performance of the phase demodulation from interference signals under different sinusoidal carrier frequencies and SNRs is numerically investigated. The piezoelectric transducer is employed to emulate the sound in the experiment to verify the effectiveness of our method. It is shown that the dynamic strain can be well reconstructed at the end of a 101.64 km fiber when the signal SNR is down to 3.234 dB. Our proposed method enables the application of the long-distance sensing in quasi-DAS systems.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001093
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Lab of Advanced Transducers and Intelligent Control Systems, Ministry of Education and Shanxi Province, Taiyuan 030024, China
2 Institute of Optoelectronic Engineering, College of Physics & Optoelectronics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
3 Fiber Optics Group, Department of Physics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa K1N 6N5, Canada
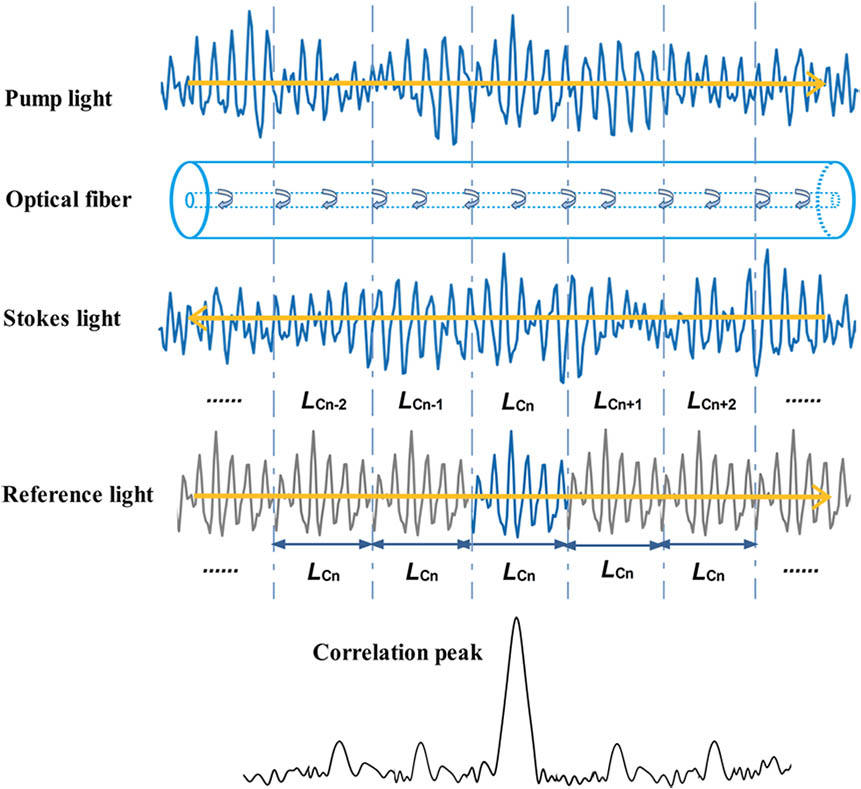
To obtain high spatial resolution over a long sensing distance in Brillouin optical correlation domain reflectometry (BOCDR), a broad laser spectrum and high pump power are used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In this Letter, we use a noise-modulated laser to study the variation of the Brillouin spectrum bandwidth and its impact on the coherent length of BOCDR quantitatively. The result shows that the best spatial resolution (lowest coherent length) is achieved by the lowest pump power with the highest noise-modulation spectrum. Temperature-induced changes in the Brillouin frequency shift along a 253.1 m fiber are demonstrated with a 19 cm spatial resolution.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.4080 Modulation 120.5820 Scattering measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 080603
1 太原理工大学物理与光电工程学院, 山西 太原 030024
2 新型传感器与智能控制教育部与山西省重点实验室, 山西 太原 030024
提出了一种利用光纤布里渊散射效应抑制光反馈半导体激光器时延特征的方法。实验研究发现,当平均功率为200 mW的混沌激光注入到长为10 km的单模光纤中,经过光纤的后向布里渊散射作用,混沌激光自相关曲线在时延105 ns处的峰值从0.251降低到0.075,互信息曲线在时延105 ns处的峰值从0.087降低到0.008。在此基础上,实验分析了注入光功率对混沌激光时延特征抑制效果的影响,结果表明,当混沌激光注入的平均功率在200~1500 mW范围内时,混沌激光的时延特征得到有效抑制;当测量次数在1~50范围内时,光纤布里渊散射对混沌激光时延特征的抑制效果较稳定。
非线性光学 布里渊散射 光反馈半导体激光器 时延特征 混沌激光





